Can a high-protein diet lead to atherosclerosis?
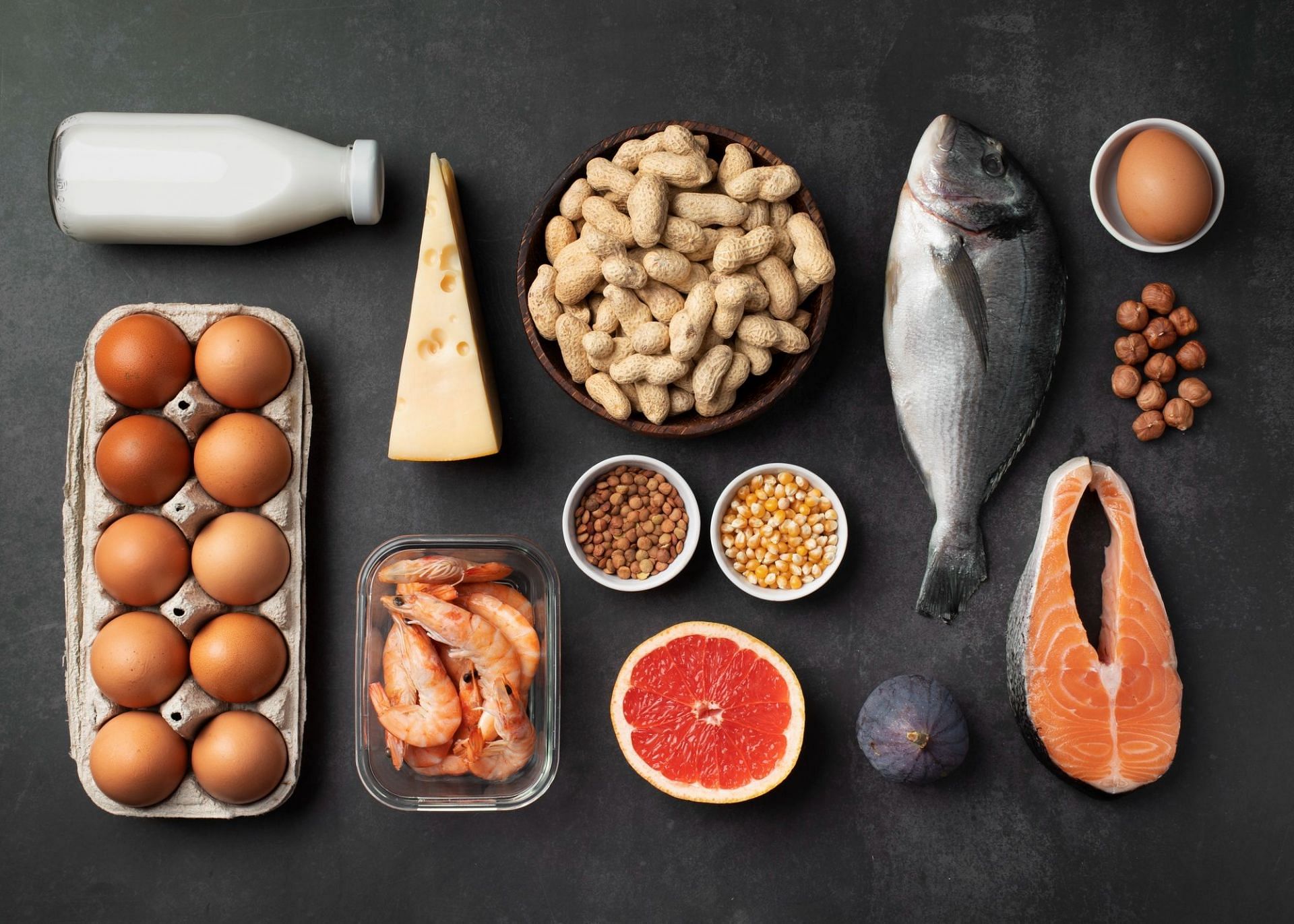

A high-protein diet is overrated and overhyped, but some follow it as a lifestyle. Individuals, who want to gain muscle or lose weight have protein-rich meals but forget that all other minerals and micronutrients are also important.
Their primary focus is only on meat or eggs, which can be a good thing, but too much of it can lead to dehydration, nausea, liver and kidney issues, heart problems and conditions like atherosclerosis.
If you do not want to stop eating protein, let's see what foods you can have and learn more about a high-protein diet and the diseases it can cause, with a focus on atherosclerosis.
What does a high-protein diet contain?

This meal usually consists of lean portions of meat like a juicy steak, eggs, pork, tofu, soya, paneer, chicken and others.
You can also add fish, as it contains omega-3 fatty acids, which can improve your heart health significantly. Cheese, low-fat milk and whole grains are also an important part of this dietary plan.
Some even take shakes or additional supplements to meet their daily requirements. Men need nearly 70 grams of protein every day, while women need roughly 55 grams daily.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a high-protein diet?
Advantages
- You can lose weight when you are on a high-protein diet, as mentioned earlier, but the weight loss is initial.
- You will feel full for longer, as the body takes longer to digest the excess protein.
- There's a gain in muscle, muscle quality and strength.
- Animal protein is good for bone health, can improve bone mass and bone quality, and helps get rid of conditions like osteoporosis and arthritis.
- Protein can help in faster recovery and is often used by athletes after workouts or when they are recovering from soreness.
Disadvantages
- There are high levels of saturated fats in high-protein meals, which can cause several risks and diseases.
- Many people get headaches and nausea when they are on this diet because of the process of ketosis.
- There's weight gain after the initial stage of weight loss, which happens as the body loses water and again gains it back.
- There's a limitation of carbs, which leads to insufficient resources for the body like fiber or other minerals and nutrients.
- This diet can cause kidney damage or failure, as the body cannot eliminate all the protein and its end products.
High-protein diet can cause atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a condition when plaque builds up inside the walls of the arteries, which cannot carry blood freely due to getting blocked. As a result, we often see blood clots which affects mainly the major arteries and restricts blood supply to the heart, brain, kidneys and other organs.
When we have a lot of protein, there's an increase in amino acids in the blood. Tjey stimulate monocytes, which are inflammatory cells, so when they get activated, a person starts suffers from atherosclerosis.
Leucine, an essential amino acid, is found mostly in animal protein, and high doses of this release monocytes, which causes atherosclerosis. So, you need to control your consumption of this amino acid, which can lead to heart diseases and organ failure.
What to eat?

A balanced diet is always the key, and switching to plant-based proteins can always work, as they contain low levels of leucine, so atherosclerosis can be avoided.
When you are having a meal, always check for your macros and micros, and not overdo your protein intake.
This protein paradox can make you question what to eat next ? If a high-protein or a high-fat diet is dangerous, what's a favorable diet? Consult your dietician, and make your die, based on your needs and BMI to avoid any health problems.




